
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, and Nano-optoelectronics Frontier Center of Ministry of Education, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Key Laboratory of Photochemical Conversion and Optoelectronic Materials, Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing, China
With the recent development of the metasurface, generating an optical vortex in optical far or near fields is realized in various ways. However, to generate vortices in both the near and far fields simultaneously is still a challenge, which has great potential in the future compact and versatile photonic system. Here, a bi-channel optical vortex generator in both the near and far fields is proposed and demonstrated within a single metasurface, where the surface plasmon vortex and the far-field optical vortex can be simultaneously generated under circularly polarized light. The ability of generating vortices with arbitrary topological charges is experimentally demonstrated, which agrees well with simulations. This approach provides great freedom to integrate different vortex generators in a single device, and offers new opportunities for integrated optical communications, trapping, and other related fields.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(6): 06000986
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, and Nano-optoelectronics Frontier Center of Ministry of Education, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, Rice University, 6100 Main Street, Houston, TX 77005, USA
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing 100871, China
Manipulation of light-matter interaction is critical in modern physics, especially in the strong coupling regime, where the generated half-light, half-matter bosonic quasiparticles as polaritons are important for fundamental quantum science and applications of optoelectronics and nonlinear optics. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are ideal platforms to investigate the strong coupling because of their huge exciton binding energy and large absorption coefficients. Further studies on strong exciton-plasmon coupling by combining TMDs with metallic nanostructures have generated broad interests in recent years. However, because of the huge plasmon radiative damping, the observation of strong coupling is significantly limited at room temperature. Here, we demonstrate that a large Rabi splitting (~300 meV) can be achieved at ambient conditions in the strong coupling regime by embedding Ag-WS2 heterostructure in an optical microcavity. The generated quasiparticle with part-plasmon, part-exciton and part-light is analyzed with Hopfield coefficients that are calculated by using three-coupled oscillator model. The resulted plasmon-exciton polaritonic hybrid states can efficiently enlarge the obtained Rabi splitting, which paves the way for the practical applications of polaritonic devices based on ultrathin materials.
Rabi splitting strong coupling transition metal dichalcogenides optical microcavity surface plasmons Opto-Electronic Advances
2019, 2(5): 190008
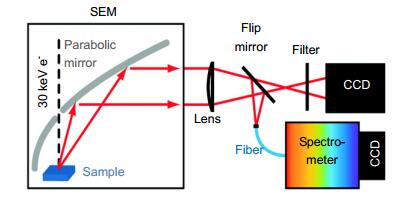
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Physics, State Key Lab for Mesoscopic Physics, Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
Cathodoluminescence (CL) as a radiative light produced by an electron beam exciting a luminescent material, has been widely used in imaging and spectroscopic detection of semiconductor, mineral and biological samples with an ultrahigh spatial resolution. Conventional CL spectroscopy shows an excellent performance in characterization of traditional material luminescence, such as spatial composition variations and fluorescent displays. With the development of nanotechnology, advances of modern microscopy enable CL technique to obtain deep valuable insight of the testing sample, and further extend its applications in the material science, especially for opto-electronic investigations at nanoscale. In this article, we review the study of CL microscopy applied in semiconductor nanostructures for the dislocation, carrier diffusion, band structure, doping level and exciton recombination. Then advantages of CL in revealing and manipulating surface plasmon resonances of metallic nanoantennas are discussed. Finally, the challenge of CL technology is summarized, and potential CL applications for the future opto-electronic study are proposed.
cathodoluminescence microscopy semiconductor metallic nanostructures surface plasmons Opto-Electronic Advances
2018, 1(4): 180007
1 广东第二师范学院物理系,广东 广州 510303
2 广东工业大学信息工程学院,广东 广州 510006
数值研究了实部具有缺陷的parity-time(PT)对称光晶格中的缺陷暗孤子。 当衍射与自散焦非线性效应 平衡时,暗孤子能够被获得;当自散焦介质中的PT对称光晶格实部被附加一个缺陷后,缺陷暗孤子也能够被获得。数值结果显示:缺陷暗孤子可以在很大参数范围内存在并能稳定传 播;PT对称光晶格实部附加的缺陷强度有一最大值,超过此值缺陷暗孤子不存 在;PT对称光晶格的虚部振幅对缺陷暗孤子的稳定性有影响。
非线性光学 缺陷暗孤子 parity-time对称光晶格 稳定性 nonlinear optics defect dark solitons parity-time-symmetric optical lattice stability
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic Engineering, Dongguan University of Technology, Dongguan 523808, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
We present a theory to investigate the existence and the propagation properties of incoherently coupled single-hump and dipole soliton pairs in self-defocusing media with parity-time symmetric lattice. These soliton pairs can exist provided that they are composed of two optical beams with the same polarization and wavelength. It is found that single-hump soliton pairs are always stable when the components copropagate in the lattice, whereas high-power dipole soliton pairs are unstable. If one of the components is absent, the propagation behavior of the other one is also studied.
190.6135 Spatial solitons 270.0270 Quantum optics Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(s1): S11901
在数字化X荧光分析仪中, 不稳定的基线电压, 会直接影响到仪器的性能, 造成能量分辨率下降。 基于此, 利用卡尔曼滤波算法, 对数字化后的X射线荧光信号进行基线估计。 由于现有的经典卡尔曼滤波、 简化sage-husa和改进sage-husa算法模型进行基线滤波的效果都不佳, 因此有必要对现有的算法进行改进和优化。 提出双重遗忘法, 建立新型的基于sage-husa自适应卡尔曼滤波算法模型。 实验结果表明, 利用该数学模型进行基线滤波, 取得了很好的滤波效果。 避免了滤波发散和基线收敛缓慢的问题, 实现了脉冲基线恢复, 提高了仪器的能量分辨率。
X荧光 卡尔曼滤波 数字基线估计 能量分辨率 X-ray fluorescence Kalman filter Digital baseline estimation Energy resolution





